Business
What is the Net Fixed Assets Formula?
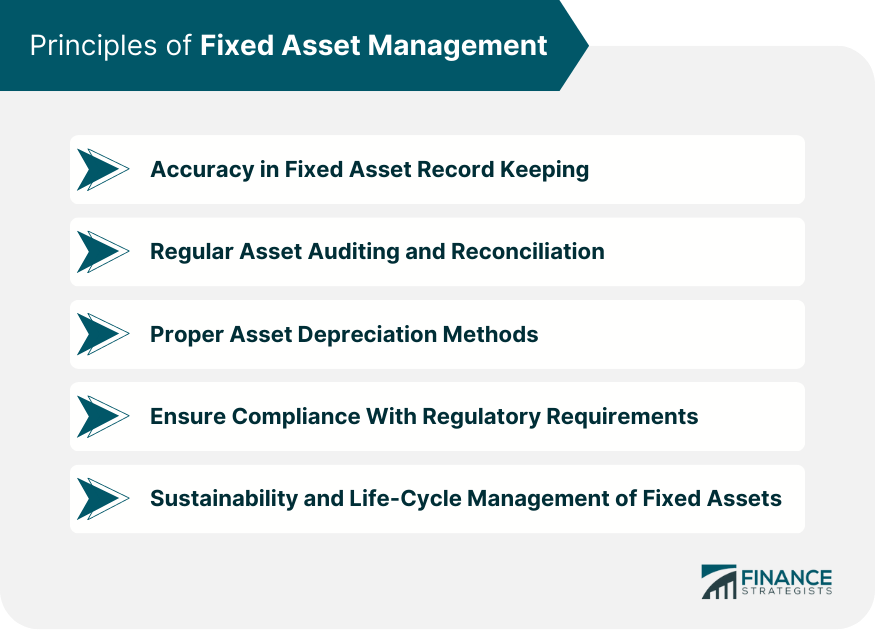
Fixed assets are a specific section of the balance sheet. This is an essential concept in terms of financial analysis since it will make it possible to determine numerous ratios and indicators, including working capital. We will answer the questions: what are fixed assets? How to calculate it? What is its use?
What are fixed assets?
Fixed assets include all assets intended to be kept in the long term by a company and which will generate future economic benefits in return. They can take one of the following types:
- Tangible fixed asset: non-monetary asset having a physical substance such as industrial equipment, tools, transport equipment, furniture, installations and fixtures;
- Intangible fixed asset: non-monetary asset without physical substance. This mainly concerns goodwill, lease rights, research and development costs, software, websites, trademarks and patents;
- Financial fixed asset: monetary asset representing a financial participation ( shares, bonds ), a loan (staff loan, loan to related entities) or a security deposit.
Unlike circulating assets, fixed assets are not destroyed by exploitation upon first use. Its loss of value (due to its use or technical obsolescence) is noted through amortization and depreciation.
Fixed assets must be financed by permanent capital. This is an important point for ensuring the financial balance of a company’s financing structure.
How to calculate fixed assets?
The gross fixed assets of a company are made up of the sum of the input values of each asset making up its assets (we speak of acquisition cost). It is calculated from the balance sheet.
Gross fixed assets = tangible assets + intangible assets + financial assets
The fixed asset can also be calculated for its net amount, in order to take into account the use of depreciable goods and their wear or obsolescence.
Net fixed assets = gross fixed assets – depreciation of tangible and intangible assets – depreciation of fixed assets
What is the use of the fixed asset?
Fixed assets are a concept that must be put into perspective taking into account the type of activity carried out. Indeed, in production companies, fixed assets represent a significant part of total assets whereas in service companies (IT service providers for example), they will not be significant. Furthermore, in holding companies, the item of financial assets will occupy an important place.
The usefulness of calculating a fixed asset lies elsewhere, and more particularly in determining the overall net working capital. It represents an intermediate step in the calculation of this essential financial indicator highlighting the balance (or not) of the financial structure of a company. In summary, it will be necessary to ensure that the fixed assets are financed at least by permanent capital (we are talking about sustainable resources) such as capital contributions, reserves, medium and long-term bank loans. The surplus eventually generated will make it possible to finance the working capital requirement then the net cash flow.
Financial ratios calculated with fixed assets
Finally, fixed assets are data used in many financial ratios called structural ratios. Here are the main ones.
- Wear rate = net fixed assets / gross fixed assets
This ratio measures the degree of wear of the company’s industrial tools. The closer it is to 1, the more recent it is. Conversely, the closer it gets to 0, the older the productive system becomes. This allows us to give an indication of the horizon for their renewal.
- Financing of fixed assets = permanent capital / (gross fixed assets – depreciation)
This ratio highlights the rate of coverage of fixed assets by the sustainable resources available to the company. It should be at least equal to 1. This concept is close to that of working capital and makes it possible to check the financial balance of investments.
- Capital intensity = tangible, intangible or financial assets / total assets
This ratio provides information on the importance of the “fixed assets” item in the balance sheet. As we mentioned above, the results must be nuanced and handled with caution since their consistency with the standard depends on the type of activity carried out by the company.
Example of fixed asset calculation
Consider the following balance sheet:
| Active | Raw | To Depreciate | Net | Passive |
| Tangible assets | 20,000 | 10,000 | 10,000 | Capital |
| Intangible assets | 10,000 | 1,000 | 9,000 | Reserves |
| Financial assets | 5,000 | 0 | 5,000 | Financial debts |
| Stocks | 15,000 | 0 | 15,000 | Payables |
| Receivables | 80,000 | 30,000 | 50,000 | Tax debts |
| Availability | 50,000 | 0 | 50,000 | Social debts |
| Total | 139,000 | 139,000 | Total |
Gross fixed assets are the total value of all fixed assets before depreciation or adjustments. In this case, the gross fixed assets would be the sum of the raw values of tangible assets, intangible assets, and financial assets:
Gross Fixed Assets = Tangible assets (Raw) + Intangible assets (Raw) + Financial assets (Raw)
= $20,000 + $10,000 + $5,000
= $35,000
Net fixed assets are the total value of fixed assets after accounting for depreciation or adjustments. In this case, the net fixed assets would be the sum of the net values of tangible assets, intangible assets, and financial assets:
Net Fixed Assets = Tangible assets (Net) + Intangible assets (Net) + Financial assets (Net)
= $10,000 + $9,000 + $5,000
= $24,000
Conclusion:
Fixed assets are data resulting from the financial analysis of the balance sheet. In particular, it makes it possible to calculate the working capital of a company in order to check whether the financial structure of its investments is healthy and balanced.
FAQs
What are the net fixed assets?
These are, for example, production equipment, computers, furniture, etc. These are materials, equipment, buildings whose value decreases with use.
How to calculate gross fixed assets?
The gross fixed assets of a company are made up of the sum of the input values of each asset making up its assets (we speak of acquisition cost). It is calculated from the balance sheet.
How to calculate the depreciation of fixed assets?
When linear depreciation is used, the depreciation rate is obtained very quickly:
- Linear depreciation rate = 1 / Actual duration of use (or tax-admissible duration of use)
- Linear depreciation annuity = (Gross value – Resale value) × Linear depreciation rate.
Read Also:
Business
Achieving Compliance and Safety Standards with Professional Control System Integration
Ensuring compliance and maintaining safety standards are crucial in industrial operations. Control system integrators play a vital role in achieving these goals through the implementation of sophisticated automation systems. These systems not only streamline processes but also ensure that all regulatory requirements are met and that workplace safety is prioritized. This blog delves into how a control integrator company helps businesses achieve compliance and safety standards through advanced control integrator technology.
The Importance of Compliance in Industrial Operations
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is essential for any business to operate legally and ethically. Regulatory bodies impose stringent guidelines to ensure that companies maintain high levels of safety, environmental responsibility, and product quality. Failing to comply with these regulations can result in severe penalties, including fines, legal action, and reputational damage.
A control system integrator ensures that all implemented systems adhere to relevant standards. By staying updated with the latest regulatory requirements, control integrators design systems that are compliant from the outset. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of non-compliance and helps businesses avoid the associated consequences.
Enhancing Safety Through Automation
Safety is a paramount concern in industrial environments where hazardous conditions and complex machinery are common. Control system integrators enhance safety by designing and implementing automated systems that reduce human intervention and mitigate risks. These systems can monitor and control processes in real time, identifying potential hazards and taking corrective actions to prevent accidents.
Control integrator technology includes safety features such as emergency shutdown systems, automated alarms, and fail-safes. These features ensure that any anomalies are quickly detected and addressed, minimizing the risk of accidents. By automating hazardous processes, control integrators help create a safer working environment for employees.
Real-Time Monitoring and Data Collection
Real-time monitoring and data collection are critical components of maintaining compliance and safety standards. Control system integrators implement systems that continuously collect data from various sensors and devices. This data provides valuable insights into the operational status of machinery and processes, enabling timely decision-making and preventive maintenance.
A control integrator company leverages advanced analytics tools to process and interpret this data. By analyzing trends and patterns, businesses can identify potential issues before they escalate. This proactive approach helps in maintaining compliance with regulatory standards and ensures that safety protocols are consistently followed.
Customizing Solutions for Specific Needs
Every industry has unique compliance and safety requirements. Control system integrators excel in providing customized solutions that address these specific needs. They work closely with businesses to understand their operational challenges and regulatory obligations, designing systems that fit seamlessly into existing workflows.
Control integrators ensure that all components of the control system, from sensors to software, are tailored to meet industry-specific standards. This customization enhances the effectiveness of the system in maintaining compliance and safety. By providing solutions that are precisely aligned with business requirements, control integrators help companies achieve their regulatory and safety goals more efficiently.
Implementing Robust Security Measures
Cybersecurity is an integral part of compliance and safety in today’s digital age. Industrial control systems are increasingly becoming targets for cyberattacks, which can compromise safety and disrupt operations. Control system integrators implement robust security measures to protect these systems from cyber threats.
A control integrator company employs advanced encryption, authentication, and access control technologies to safeguard control systems. Regular security assessments and updates ensure that the systems remain resilient against emerging threats. By prioritizing cybersecurity, control integrators help businesses protect their operations and comply with data protection regulations.
Training and Support
Effective training and support are essential for maintaining compliance and safety standards. Control system integrators provide comprehensive training programs to ensure that employees understand how to operate and maintain the automated systems. This training covers both the technical aspects of the system and the regulatory requirements that must be adhered to.
Control integrators also offer ongoing support to address any issues that may arise. This includes regular maintenance, troubleshooting, and updates to ensure that the systems continue to operate efficiently and in compliance with regulations. By providing continuous support, control integrators help businesses maintain high standards of safety and compliance.
Ensuring Long-Term Compliance and Safety
Achieving compliance and safety standards is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process. Control system integrators play a crucial role in ensuring long-term compliance and safety through continuous monitoring, regular updates, and proactive maintenance. Their expertise ensures that systems are always aligned with the latest regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
By leveraging control integrator technology, businesses can stay ahead of regulatory changes and ensure that their operations remain safe and compliant. Control integrators help create a culture of safety and compliance, where continuous improvement and vigilance are integral to daily operations.
Professional control system integration is essential for achieving and maintaining compliance and safety standards in industrial operations. Control system integrators provide the expertise, technology, and support needed to ensure that businesses operate within regulatory guidelines and prioritize safety. Through real-time monitoring, customized solutions, robust security measures, and ongoing support, control integrators help businesses achieve their compliance and safety goals, contributing to overall operational excellence.
Business
What is an invoice? The complete guide

What is an invoice? An invoice is a request for payment issued by a seller to the buyer of goods or services after the sale, detailing the goods supplied or work performed, and the amount to be paid in return.
Definition of an invoice
The invoice is an accounting document that proves a purchase or sale. It lists the goods and services provided by your company, and at the same time indicates their price, as well as the total amount to be paid by the buyer.
The invoice is therefore essential since it is the document which identifies the creditor (you) and the debtor (your customer) and serves as a request for payment. But to be valid, it must meet certain conditions.
According to current legislation, the invoice is obligatory. Please note that the buyer has the right to claim one if it has not been sent to him.
Brief history of invoices
Before contemporary bills, counting sticks were used, followed by inscriptions on bones, such as the Ishango stick dating back approximately 20,000 to 25,000 years in the Congo.
The first invoice-like documents come from the Middle East: the Sumerians developed cuneiform around 3200 BC. recording on clay tablets various transactions, including the receipt of livestock.
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th century brought notable improvements in invoicing, and then accounting machines in the 19th century revolutionized this area.
In the 20th century, the appearance of logos on invoices marked a further step, before EDI in the 1960s facilitated the exchange of financial documents. Since the 1990s, invoices have migrated to web platforms.
Invoice functions
Everything has its reason for being and the invoice is no exception: you will be surprised to learn the importance of this document. Among the most significant functions of a typical invoice are that it allows you to:
Maintain transaction history: Probably the most important function of all, the invoice leaves a distinct written record of business activity. It indicates who is responsible for the provision of services or delivery of goods, payment details and the conditions of execution of the contract.
Helping accountants: What is an invoice in accounting? Following the previous point, invoices are essential for the proper maintenance of general accounting. These documents are used to determine the total amount of accounts payable and creditors. In addition, invoices are used to record taxable revenue, which helps a business or self-employed person declare their income. Good invoicing can be an additional asset in the event of an audit.
Legal representation function: Invoices can serve as a reliable mediation for possible disputes between a buyer and a seller. In this way, the risks of fraudulent activities on either side are significantly reduced.
A powerful tool for analysis: Invoices help collect information about customer purchasing habits, the most commonly ordered types of goods or services, peak periods, and more. This data will be very useful in planning the future development of the company.
An invoice can fulfill a wide range of business tasks. It provides clear order information to both parties and leaves virtually no room for fraud.
What is the role of invoice?
The invoice is an essential document which will allow:
- monitoring the various commercial transactions, essential for your accounting, your tax return, but also to know your financial situation precisely;
- to prove what you actually earned;
- to justify the agreement concluded with the client. To do this, you will need to present it clearly to avoid misunderstandings;
- to request payment from your buyer. You will thus receive the money due for your work;
- to take action in the event of unpaid debts ;
- to promote your activity and develop the image of your company through a logo or links to social media.
What are the different types of invoices?
There are several types of invoices :
- The standard invoice: this is the most common document. It can be used for several sectors of activity and consists of a very basic format containing all the necessary information.
- Commercial invoice: it is used in international trade for shipping goods from one country to another.
- The proforma invoice: it gives the buyer an estimate of the price of the products or services.
- The closing invoice: which closes a contract between a service provider and a client.
- The credit note: it allows you to cancel or modify an invoice already established.
- The deposit invoice: it allows you to justify the amount paid upstream of the delivery or production of a good or service.
What items should be included on the invoice?
For the invoice to be valid, it must include a certain number of mandatory information :
- The mention “ invoice ”,
- Invoice number,
- Date of issue of the invoice,
- The name or company name of your establishment,
- The head office address, as well as the billing address (if different),
- The VAT number, the SIREN number and the legal form of your company,
- Customer’s name and contact details (if the billing address and delivery address are different, you must enter both),
- Customer’s VAT identification number if it is a professional,
- The detailed account of each service and/or product, in quantity and unit price excluding tax,
- The price of labor,
- Total amount to be paid excluding tax,
- The applicable VAT rates and amounts, as well as the total amount all taxes included,
- Payment conditions (payment deadlines, amount of any deposit),
- Penalties for late payment may apply.
How to create an invoice online?
Save time and make it easier to create your invoices with online invoicing software.
Simply let the software guide you when creating your first invoice.
If you use software that complies with the anti-fraud law, you have the assurance of creating a clear invoice that complies with the requirements of regulations.
Invoice with or without VAT and choose the legal notice that corresponds to your status (self-liquidation, self-employed, exemption, reduced VAT, etc.).
When you provide your legal, product and customer information, it is recorded in your database.
Thus, all subsequent invoices will automatically include your contact details and legal notices and you will be able to import your products and customers in just a few clicks.
Tips for writing an invoice
First of all, be as clear and complete as possible in the description of your services and/or products. The customer wants to know concretely what they are buying! A beautiful presentation also makes all the difference and directly reflects your professionalism.
On the other hand, know that using invoicing software will allow you to save time and avoid oversights. This very practical tool not only guarantees you compliant invoices, but also considerably facilitates administrative management. In addition, your documents can be viewed from anywhere, and tracking and reminders are greatly simplified.
In summary
The invoice is a commercial, legal and accounting document established by a professional during the sale of goods or the provision of services.
This document, published in two copies, proves that the sale took place.
To be admissible, an invoice must contain a certain number of mandatory information. You can add other information that you deem relevant, as well as your conditions of sale.
To save time editing your invoicing documents and avoid errors, we advise you to use invoicing software.
Read Also:
3 Types of Invoices in Business Transactions, What Are They?
Business
Pros and Cons of BYOD: Opportunities and Risks For Companies

With increased remote work from home offices during the previous pandemic, the use of private devices has also become more and more established. Even if this solution initially seems helpful for companies and employees, the concept poses some risks and dangers for IT security.
We will show you how the use of your own technical devices can be combined with maintaining data security and what companies need to pay attention to. Learn about the pros and cons of BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies to make informed decisions for your organization.
What should you consider when it comes to data security
Access to sensitive company data from private devices often poses threats to a company’s IT security situation. In principle, any digital device that has a network connection can pose a risk to IT security – whether it is currently used hardware and software or old devices that are still in the network. Private gadgets used in BYOD only have limited control: after all, they continue to be used in non-company networks and for personal purposes. This raises the risk of malware such as rootkits, and company data stored may be more vulnerable to cybercriminal access. That’s why companies should develop a comprehensive security concept before they allow the use of third-party devices. All security guidelines for handling can be recorded in this so that the “Bring your own device” concept can be successfully introduced and all risks can be minimized as early as possible.
Explore The Pros and Cons of BYOD
Pros of BYOD
Working according to the bring your own device principle has numerous advantages for users and institutions. Employees who can bring their personal mobile device into the company do not need to get used to a different operating system. You put together the features of your laptop according to your personal wishes. This increases employee satisfaction.
Using your own mobile device for work allows for greater flexibility. When smartphones or tablets are used, employees gain greater mobility .
Bring Your Own Device means cost savings for companies. There is no need to purchase new computers if employees use their own.
Working with your own, familiar device in schools, universities or libraries means greater user-friendliness . With good WiFi coverage, smartphones, tablets or laptops can be used flexibly and mobilely in different locations, unlike stand-alone PCs. Likewise, there is no need to invest in a large part of the IT equipment for educational institutions because they do not have to provide computers.
Cons of BYOD
The bring your own device principle also has disadvantages for companies and institutions. A serious factor is the lack of data security when accessing an internal network or sensitive company data. Using your own devices means a high degree of heterogeneity or diversity in a company’s hardware and software equipment. The different laptops, smartphones or tablets require more effort for IT management, which puts the cost savings when purchasing company-owned devices into perspective.
Data security with the bring your own device principle
Bring Your Own Device complicates administration and control, meaning employees’ private devices represent a security gap for the company’s internal network.
If a private laptop is affected by malware and is connected to the network of a facility, a Trojan can read the entries on the keyboard and thus logins and passwords. This is how hackers gain access to sensitive data. If the network of a company or institution is open to external access – for example via cloud services – then outsiders can gain access. This also applies to password-protected logins.
Bring Your Own Device and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
There is also a legal aspect. With Bring Your Own Device, personal or company-internal data is accessed and stored on a private device. This does not comply with the guidelines of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). It must be legally clarified how data and business secrets are handled. In addition to reduced data security, the flexible use of private devices also means stress for employees. If you use your laptop in your free time and can be reached at any time, it is difficult to separate your private and work life.
Advantages
- Efficient work on your own device
- High employee satisfaction
- High user-friendliness
- Flexibility & mobility
- Cost savings for companies
Disadvantages
- Lack of data security
- Security gap for the company network
- Legal objection: GDPR
- Heterogeneous hardware and software
- Difficult administration for IT
Guidelines and Safeguards for Bring Your Own Device
When applying the bring your own device approach, it is important to weigh up the advantages and disadvantages as well as the costs and benefits. In addition to small hurdles such as the fact that software such as Microsoft Office on private laptops is not licensed for commercial use in companies, ensuring data security requires a certain amount of effort. It is worth setting up internal company guidelines for these purposes. The basic procedures include regularly updating the operating system, using a virus scanner and uniform software to protect against malware.
What are the future trends and directions of BYOD?
Future trends and trends in BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) are constantly evolving depending on technological advances, changes in ways of doing business and the needs of employees. Here are the possible future trends and directions of BYOD:
1. Greater Mobility and Flexibility:
With mobile device technology constantly evolving, BYOD policies can become even more mobile and flexible. The spread of 5G and next generation connection technologies will provide employees with access to higher speed data transmission and stronger connections. This can enable the workforce to work more efficiently without being tied to the local office.
2. Increasing Security Measures:
With the increasing use of BYOD, security concerns are also increasing. In the future, businesses will adopt stronger security measures and data protection strategies for BYOD policies. By using security technologies such as biometric authentication, multi-factor authentication and remote data encryption, business data will be protected more securely.
3. Compliance and Regulations:
BYOD use triggers various compliance requirements such as data protection regulations and personal data privacy laws. In the future, businesses may have to update BYOD policies and improve data protection processes to ensure such compliance.
4. More BYOD Support and Consultancy:
As BYOD becomes more complex, companies will need more consultancy and expertise to develop, manage and support BYOD policies. Cybersecurity consultants and technology providers will become more important to offer appropriate BYOD solutions to organizations.
5. BYOD and IoT (Internet of Things) Integration:
With the increasing use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, BYOD policies can expand to cover more device types. Employees can also be integrated to manage IoT devices and monitor their data through BYOD devices.
6. Virtualization and Cloud-Based Solutions:
Virtualization technology and cloud-based applications can help in the successful implementation of BYOD policies. It can improve security and data protection measures by providing access to business clients through employees’ personal devices. Likewise, cloud-based applications can offer a more secure environment for accessing data and collaborating.
Conclusion:
There are many pros and cons that should be analyzed before adopting a BYOD strategy. A BYOD strategy can save money and increase productivity by promoting familiarity with a work device. However, such a strategy may also entail certain risks for the company. Before implementing a BYOD strategy, both employees and employers should thoroughly research the policies and risks to familiarize themselves with the key advantages and disadvantages.
FAQs
What should be contained in a BYOD policy?
BYOD policies must take into account general or industry-specific compliance regulations . Even if employees use personal devices, the company must still ensure that data is protected. They must also understand the liability linked to compromised data.
What security challenge does BYOD pose for networks?
The biggest challenge to widespread BYOD adoption is security, closely followed by compliance issues . Security is not an aspect that can be ignored; Using corporate apps on employee-owned mobile devices can lead to data leakage and connectivity issues.
Read Also:
-

 Top2 years ago
Top2 years ago2022 US House committee releases Trump’s tax returns, capping a years-long battle
-

 Auto1 year ago
Auto1 year agoTop Porsche Taycan Incentives: Save Big
-

 Business1 year ago
Business1 year agoBeware Of Fake Emails And Fake Apple Pay Images
-

 Business1 year ago
Business1 year agoDoes 7-Eleven Take Apple Pay
-

 Top2 years ago
Top2 years agoInterview With Niantic CEO John Niantsullivan
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoUSPS EMPLOYEE ASSISTANCE PROGRAM SERVICES AND BENEFITS
-
 Top1 year ago
Top1 year agoUnderstanding the Healing Process of Nose Piercings – A Comprehensive Guide
-

 Cryptocurrency1 year ago
Cryptocurrency1 year agoBridging the Gap: Binbex Futures








